Understanding the S&P 500
How do i invest in the s&p 500 – The S&P 500, or Standard & Poor’s 500, is a stock market index tracking the performance of 500 large-cap U.S. companies. It’s widely considered a benchmark for the overall U.S. stock market and a popular investment vehicle for both individual and institutional investors. Understanding its composition, historical performance, and comparison to other indices is crucial before investing.
S&P 500 Index Composition
The S&P 500 is a market-capitalization-weighted index, meaning larger companies hold more weight. The index covers approximately 80% of the total U.S. equity market capitalization. Companies are selected based on market capitalization, financial viability, and industry representation, ensuring a diversified representation across various sectors like technology, healthcare, finance, and consumer goods. The index is regularly reviewed and rebalanced to reflect changes in the market landscape.
Historical Performance of the S&P 500
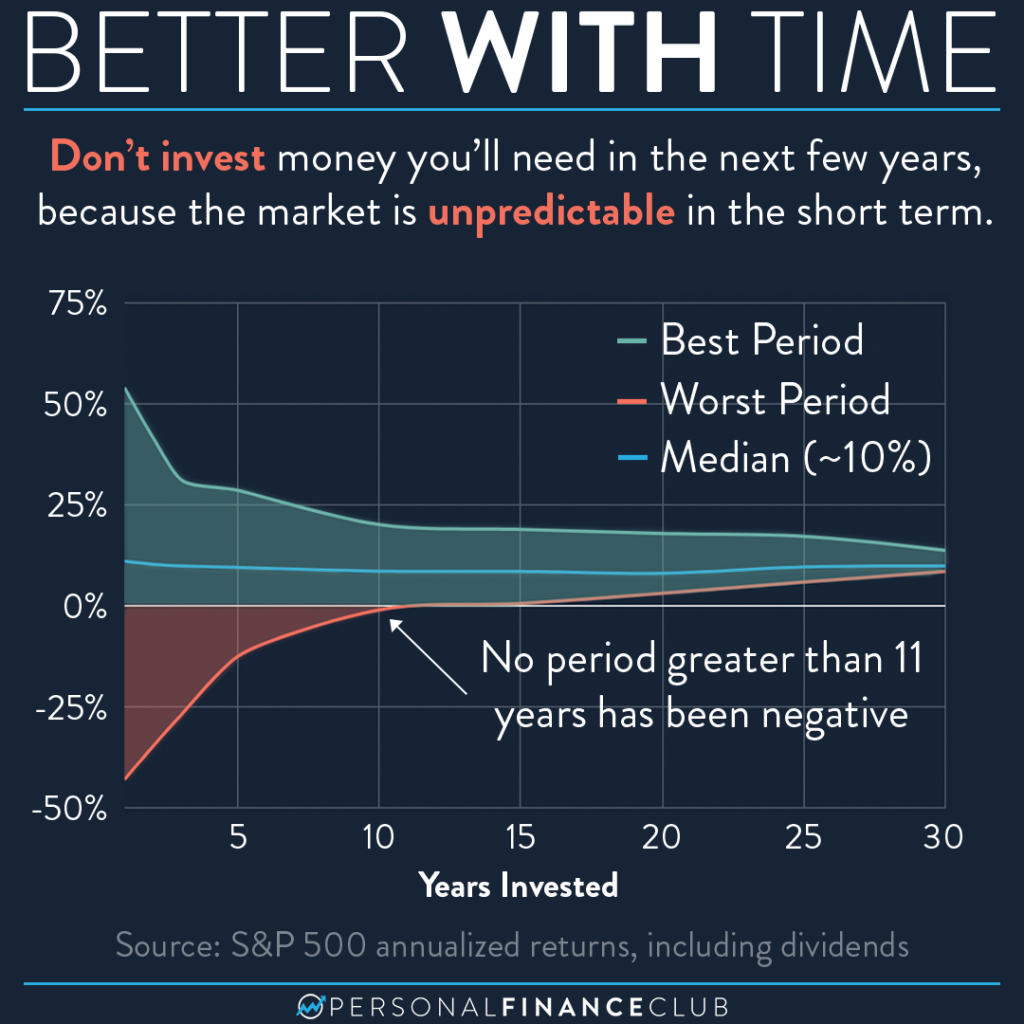
The S&P 500 has demonstrated strong long-term growth over its history. While experiencing periods of volatility and decline, the index has historically delivered positive returns over the long term. For example, from 1926 to 2022, the average annual return of the S&P 500 was approximately 10%, although this is not a guarantee of future performance. It’s important to remember past performance is not indicative of future results.
S&P 500 Compared to Other Major Market Indices
The S&P 500 is often compared to other major indices like the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) and the Nasdaq Composite. While all three track U.S. equities, they differ in composition and weighting. The DJIA consists of 30 large, well-known companies, while the Nasdaq Composite focuses on technology and growth stocks. The S&P 500 provides broader market representation compared to the DJIA and a more diverse sector representation than the Nasdaq.
Risk and Reward Comparison: S&P 500 vs. Individual Stocks
| Factor | S&P 500 | Individual Stocks |
|---|---|---|
| Risk | Moderate (diversified portfolio) | High (individual stock volatility) |
| Reward Potential | Moderate (market-based returns) | High (potential for significant gains, but also losses) |
| Diversification | Inherent (500 companies) | Requires active diversification |
| Management Effort | Low (passive investment) | High (requires research and monitoring) |
Investment Methods: How Do I Invest In The S&p 500
Several methods exist for gaining exposure to the S&P 500. Each offers unique advantages and disadvantages regarding fees, diversification, and management effort. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the most suitable approach based on individual investment goals and risk tolerance.
Methods for S&P 500 Exposure

Investors can access the S&P 500 through exchange-traded funds (ETFs), mutual funds, or by purchasing individual stocks comprising the index. Each method has its own set of pros and cons.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): ETFs are passively managed funds that track the S&P 500. They offer low expense ratios and high liquidity. However, they don’t offer active management.
- Mutual Funds: Mutual funds also track the S&P 500, but they are actively or passively managed. Actively managed funds may have higher expense ratios but aim for outperformance. Passively managed mutual funds are similar to ETFs.
- Individual Stock Purchases: Buying individual stocks from the S&P 500 requires extensive research and monitoring. This approach offers higher potential returns but also carries higher risk and requires more active management.
Fees Associated with S&P 500 Investment Methods
| Investment Method | Expense Ratio (Typical Range) | Transaction Fees (Typical) | Other Fees |
|---|---|---|---|
| ETFs | 0.05% – 0.15% | Variable, depending on brokerage | Potentially small account maintenance fees |
| Mutual Funds | 0.1% – 2% | May be included in expense ratio | Potential front-end or back-end loads |
| Individual Stocks | N/A | Variable, depending on brokerage | Commission fees per trade |
Reputable Brokerage Firms
Several reputable brokerage firms offer investment options for accessing the S&P 500. These include, but are not limited to, Fidelity, Schwab, Vanguard, and TD Ameritrade. It’s crucial to research and select a brokerage that aligns with your investment needs and preferences. Consider factors like fees, platform usability, and research tools.
Risk Management and Diversification
While the S&P 500 offers diversification across various sectors, it’s essential to understand and manage the inherent risks. Diversification strategies are key to mitigating these risks and building a resilient investment portfolio.
Inherent Risks of S&P 500 Investment
Investing in the S&P 500 carries market risk, meaning the value of your investment can fluctuate due to overall market conditions. Economic downturns, geopolitical events, and inflation can all negatively impact the index’s performance. It is crucial to have a long-term perspective when investing in the S&P 500.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Several strategies can help mitigate risk when investing in the S&P 500. These include dollar-cost averaging (discussed later), diversification beyond the S&P 500, and having a well-defined investment timeline.
Benefits of Diversification
Diversification reduces the impact of any single investment’s underperformance on your overall portfolio. While the S&P 500 itself offers some diversification, holding assets outside the index can further reduce risk. This can include international stocks, bonds, real estate, and alternative investments.
Diversification Strategies Beyond the S&P 500
- Invest in international stocks to reduce dependence on the U.S. economy.
- Allocate a portion of your portfolio to bonds for stability and lower volatility.
- Consider real estate investments for long-term growth and potential rental income.
- Explore alternative investments like commodities or private equity (if appropriate for your risk tolerance).
Factors to Consider Before Investing
Before investing in the S&P 500, it’s crucial to assess your personal financial situation, investment goals, and risk tolerance. Understanding these factors will guide your investment strategy and ensure it aligns with your overall financial plan.
Understanding Your Financial Goals
Define your investment objectives. Are you saving for retirement, a down payment on a house, or other goals? This clarity will help determine your investment timeline and risk tolerance.
Investor Profiles and Investment Strategies
Different investor profiles have different strategies. A young investor with a long time horizon might tolerate more risk and invest a larger portion in stocks. An older investor nearing retirement might prefer a more conservative approach with a larger allocation to bonds.
Impact of Time Horizon
Your investment timeline significantly impacts your investment strategy. Longer time horizons allow for greater risk-taking, as there’s more time to recover from potential market downturns. Shorter time horizons often require a more conservative approach.
Calculating Risk Tolerance
Risk tolerance is your ability and willingness to accept potential losses in pursuit of higher returns. Several online questionnaires and tools can help assess your risk tolerance. Understanding your risk tolerance is crucial for selecting appropriate investments.
Long-Term Investment Strategies
A long-term investment approach is generally recommended for S&P 500 investments. Strategies like dollar-cost averaging can help mitigate risk and maximize returns over time.
Dollar-Cost Averaging
Dollar-cost averaging involves investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of market fluctuations. This strategy reduces the risk of investing a lump sum at a market peak. It also helps to average the cost basis over time.
Benefits of a Long-Term Approach
A long-term approach allows you to ride out market fluctuations and benefit from the historical tendency of the S&P 500 to grow over time. It reduces the emotional impact of short-term market volatility.
Adjusting Investment Strategy Based on Market Conditions
While a long-term strategy is recommended, market conditions can warrant adjustments. For example, during periods of high volatility, one might consider increasing their bond allocation for stability. During periods of economic growth, one might consider increasing their stock allocation. However, significant shifts should be made cautiously and with consideration of one’s overall financial plan.
Long-Term Growth Potential of the S&P 500 (Illustrative Example)
Imagine investing $10,000 in the S&P 500 index. Assuming an average annual return of 7% (a more conservative estimate than the historical average, accounting for potential downturns), after 10 years, your investment could grow to approximately $19,671. After 20 years, it could grow to approximately $38,696. This is a simplified illustration and doesn’t guarantee future performance. Actual returns will vary.
Resources and Further Learning

Numerous resources are available for those interested in learning more about investing in the S&P 500. These include reputable financial websites, educational materials, and books written by financial experts.
Reliable Financial Websites
- Investopedia
- The Wall Street Journal
- Yahoo Finance
- Bloomberg
Books and Articles on S&P 500 Investing

Numerous books and articles delve into S&P 500 investing strategies. Searching online book retailers or academic databases will yield a wide selection of relevant materials. Look for titles focused on index fund investing and long-term strategies.
Reputable Financial Advisors, How do i invest in the s&p 500
Consider consulting a fee-only financial advisor for personalized guidance. Fee-only advisors are compensated solely by their clients, eliminating potential conflicts of interest. You can find fee-only advisors through the National Association of Personal Financial Advisors (NAPFA).